Let’s say that our example company turned over the $2,200 accounts receivable to a collection agency on March 5, 2019 and received only $500 for its value. The difference between $2,200 and $500 of $1,700 is the factoring expense. Interest on a note receivable is calculated by multiplying the principal balance of the note by the interest rate and by the number of days that have elapsed since the last interest payment was made divided by 365.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
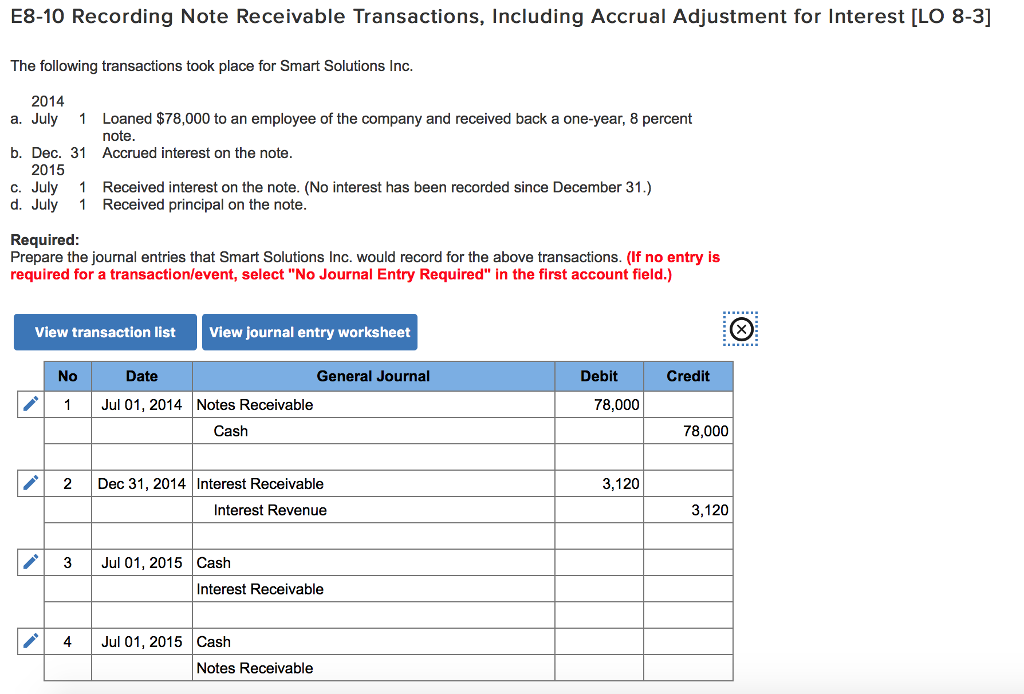
- A Note Receivable is recorded when a company is on the “receiving” side of a debt.
- Using our example, if the company was unable to collect the $2,000 from the customer at the 12-month maturity date, the following entry would occur.
- Interest revenue from year one had already been recorded in 2018, but the interest revenue from 2019 is not recorded until the end of the note term.
- The straight-line method is easier to apply but its shortcoming is that the interest rate (yield) for the note is not held constant at the 12% market rate as is the case when the effective interest method is used.
- Interest on a Note is generally recorded at the time the interest is earned.
Determining present values requires an analysis of cash flows using interest rates and time lines, as illustrated next. Notes receivables describe promissory notes that represent loans paid from a company or business to another party. The note comes with a promise from the borrower that it will repay the lender in the future. For example, a company may have an outstanding account receivable in the amount of $1,000. The customer negotiates with the company on June 1 for a six-month note maturity date, 12% annual interest rate, and $250 cash up front. Dino-Kleen, a customer of Terrance Inc. owes a $10,000 invoice that is past due.
Notes Receivable Terms
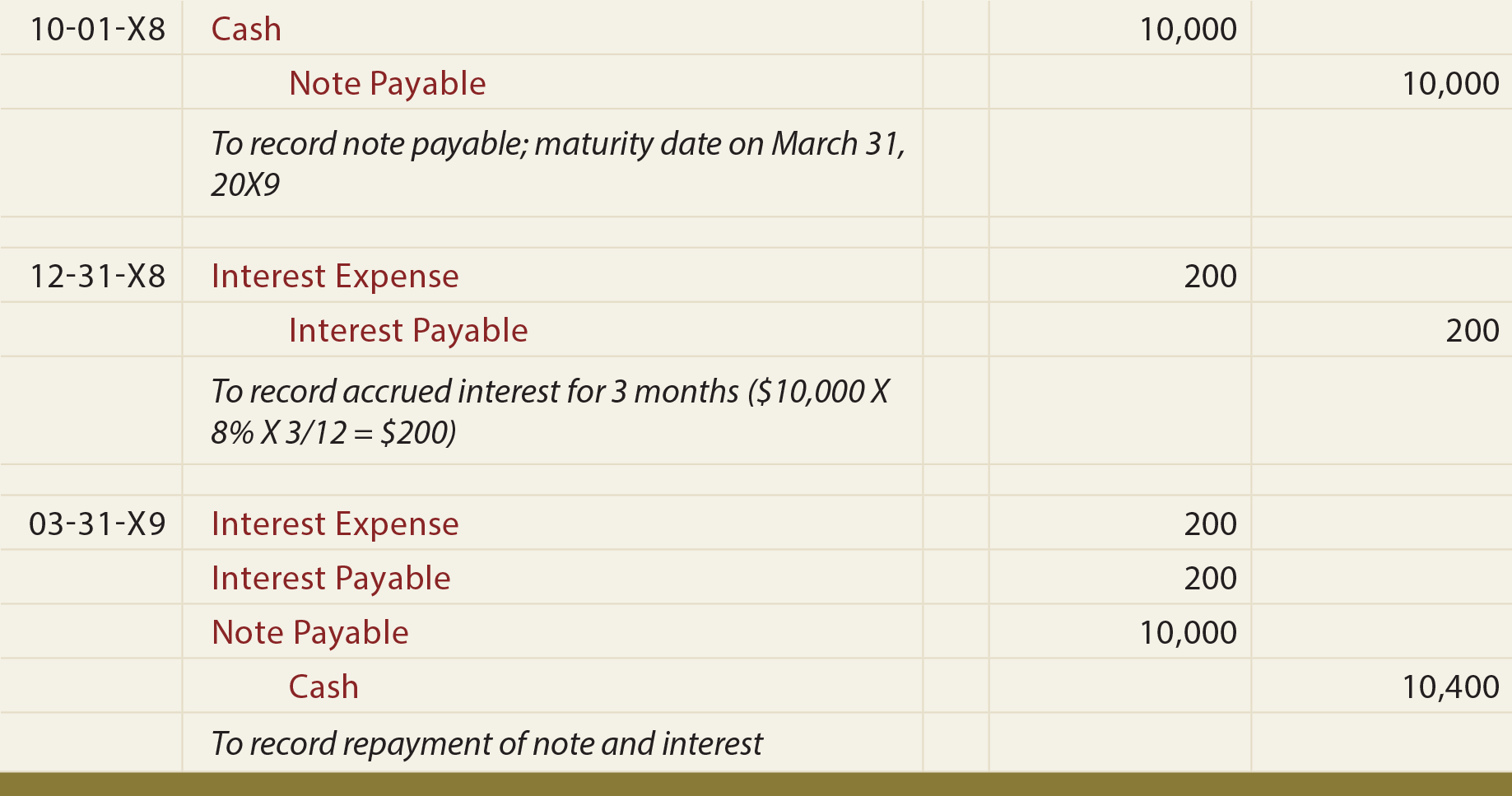
This is because not all the sales made to a particular customer are recorded in the customer’s subsidiary accounts receivable ledger. There are several types of notes receivable that arise from different economic transactions. For example, trade notes receivable result from written obligations by a firm’s customers. The note has now been completely paid off, and ABC has recorded a total of $246 in interest income over a three-month period. Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. This is important for accurate financial reporting and compliance with…
How is Interest on a Note Recorded?
If a company is selling to its customer and issuing a Note Receivable rather than an Accounts Receivable, a Revenue account would be credited to record the revenue. When interest will be paid on a Note Receivable is specified in the promissory note. The note may specify that the interest is due at the maturity of the note. Or, it may specify that interest will be due at certain points during the note’s duration (monthly, quarterly, semi-annually). Time represents the number of days (or other time period assigned) from the date of issuance of the note to the date of maturity of the note. As shown above, the note’s market rate (12%) is higher than the stated rate (10%), so the note is issued at a discount.
Notes receivable can convert to accounts receivable, as illustrated, but accounts receivable can also convert to notes receivable. The transition from accounts receivable to notes receivable can occur when a customer misses a payment on a short-term credit line for products or services. In this case, the company could extend the payment period and require interest. You should classify a note receivable in the balance sheet as a current asset if it is due within 12 months or as non-current (i.e., long-term) if it is due in more than 12 months. Notes receivable are financial assets of a business which arise when other parties make a documented promise to pay a certain sum on demand or on a specific date. Notes receivable are different from accounts receivable because they are formally documented and signed by the promising party, known as the maker of the note, to the party who receives the payment, known as the payee.
Ask Any Financial Question
The payer, or the marker, is the borrower who gets the loan from the payee. So far, our discussion of receivables has focused solely on accounts receivable. Companies, however, can expand their business models to include more than one type of receivable. This receivable expansion allows a company to attract a more diverse clientele and increase asset potential to further grow the business. The accounts receivable is just as valid a claim as are the notes receivable, as well as the interest. In some cases, the note is received in one accounting period and collected in another.
Furthermore, by transferring the note to Accounts Receivable, the remaining balance in the notes receivable general ledger contains only the amounts of notes that have not yet matured. When the how to file a business tax extension online payment on a note is received, Cash is debited, Note Receivables is credited, and Interest Revenue is credited. When a note is received from a customer, the Notes Receivable account is debited.
Notes Receivable due in more than one year are listed in the Long-term Asset section of the Balance Sheet. Where I/Y is interest of .75% each month (9%/12 months) for six months. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.